• Along with the numerous benefits of big data, come the potential risks too. Trusting big data blindly could result in disappointing outcomes.

The real wealth of any organization is their customers. To meet the customer needs and to seek new ways to fulfill their ever-increasing demands, organizations leverage big data analytics to offer tway better services than their competitors. Besides, companies implement big data analytics to make all business processes run efficiently. However, if organizations do not apply the right data governance strategy, then their investment in big data analytics is at high risk. This blog post aims to bring before organizations the risks associated with trusting big data blindly and the solutions for these risks.
What can blindly trusting big data lead to?
Trusting big data blindly could result in unexpected data loss and the associated costs, which could have a negative impact on the oversall performance of an organization. There is a need for data governance strategy that can ensure that the data available to an organization is accurate, homogenous, and secure. Recent research on big data has some interesting facts to state:
- “Nearly 40% of all company data is found to be inaccurate.”
- “66% of organizations believe they’re negatively affected by inaccurate data.”
These statistics are an answer for all those data officers who still question the need for a data governance startegy. As vast chunks of data pour into any organization, they find it difficult to secure the data, provide accurate and consistent analytical results, and carry out all business operations efficiently. Furthermore, a significant volume of customer data also gathers with these organizations. If a business fails to find relevant patterns in data, gain customer insights ,and offer talior made services, then the business is bound to fail.
What is the solution…?
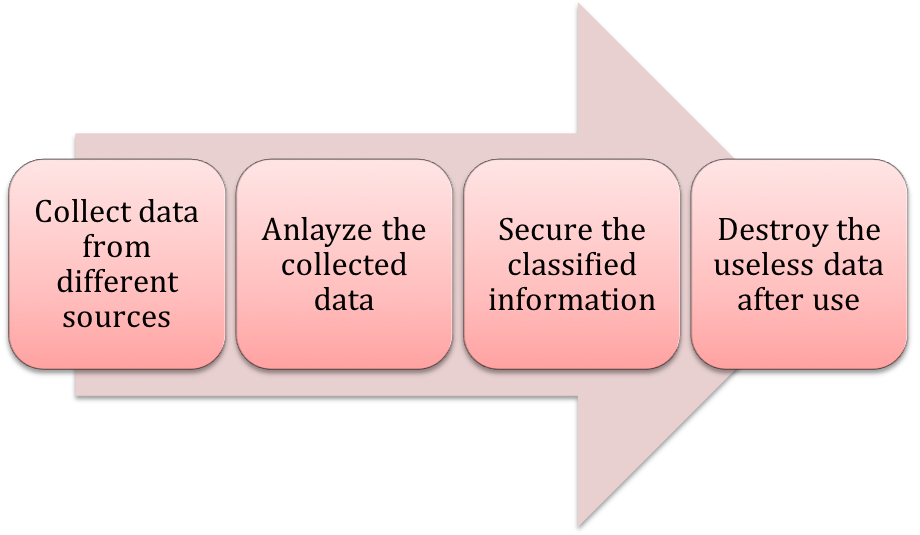
- Enterprises should trust big data only after implementing a data governance strategy in their business. Let us break the data governance strategy into logical steps: Sourcing – This is the first and foremost step in the implementation of a data governance strategy. Before implementing big data analytics, companies must determine the sources of data. Organizations should analyze the data coming from different sources, such as customer data, marketing campaign data, product data, and vendor data, before applying analytics to it.
- Analysis – Once data from all the sources is successfully collected, the second step in the strategy is data analysis. This includes eradication of duplicate data, analysis of market trends based on business goals, and the evaluation of the marketing campaign.
- Privacy – Through data analysis, companies will get a comprehensive idea of all the sensitive data in the organization. The third step is limiting the dissemination of classified information using big data analytics.
- Destruction – The fourth and the final step is to destroy data once it is utilized. Maintaining data even after its due use will increase the risk of the data turning dark, resulting in issues such as increased storage, enhanced cost, data breaches.
The advent of advanced technologies like big data has solved numerous issues and challenges. However, it is vital that organizations recognize the risks associated with these technologies as well, and address them at the earliest.